
Binoculars have been invaluable tools for exploration and observation since their invention in the early 17th century. These remarkable optical devices have allowed us to gaze at distant objects, uncover hidden details, and connect with our surroundings in ways previously unimaginable.
Today, we embark on a journey to answer a frequently asked question: “How far can you see with 10×50 binoculars?” In our quest for understanding, we’ll explore the historical roots of binoculars, delve into the intricacies of magnification and lens specifications, and unravel the concepts of “angle of view” and “field of view” to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic at hand.
Historical Origins: The Birth of Binoculars
Binoculars have a long and fascinating history that dates back many centuries. The concept of magnification can be traced back to the invention of corrective eyeglasses in 13th century Italy. These early devices utilized convex lenses to magnify objects close to the user’s eyes, allowing for improved vision.
The modern design of binoculars, as we know them today, was developed over 100 years ago. In 1825, J. P. Lemiere introduced the first binoculars, which revolutionized the way people observed the world around them. The technology behind binoculars continued to advance, and in 1854, Ignazio Porro patented the Porro prism system, which is still used in modern binoculars to achieve a right-to-left view.
A significant milestone in the history of binoculars occurred in the early 20th century when Zeiss combined two monocular telescopes to create binoculars that provided a natural and three-dimensional image. This breakthrough design marked a major advancement in binocular technology.
Today, binoculars are widely used for a variety of applications, including nature observation, birdwatching, hunting, and stargazing. Modern binoculars come in various sizes, designs, and optical configurations to cater to different needs and preferences. Advancements in lens coatings, prism systems, and materials have led to improved image quality, durability, and portability.
The history of binoculars showcases a continuous journey of innovation and refinement to meet the ever-growing demands of users for clearer and more immersive viewing experiences.
Understanding Magnification: The Power of Zoom
Different magnifications in binoculars, such as 8x, 10x, and 12x, offer varying benefits and drawbacks, making each option suitable for different scenarios. Here’s an overview of the common magnifications and their characteristics:
8x Magnification
Advantages: Binoculars with 8x magnification provide a wider field of view, allowing you to observe a larger area. The image stability is generally better due to lower magnification, resulting in less noticeable hand shake and easier tracking of moving objects. They also tend to have better low-light performance.
Disadvantages: The level of detail may not be as high as with higher magnifications, making it more challenging to view distant or small objects in great precision. They may also have limitations when it comes to observing fine details in certain scenarios, such as birdwatching.
When to Choose 8x: Opt for 8x magnification if you prioritize a wider field of view, easier image stability, and better low-light performance. These binoculars are suitable for activities like nature observation, wildlife spotting, and general-purpose use.
10x Magnification
Advantages: Binoculars with 10x magnification offer increased detail and allow for better observation of distant objects. They strike a balance between magnification and a still manageable field of view, providing a good compromise for various applications. They can be helpful for activities like birdwatching, sports events, and wildlife spotting.
Disadvantages: The higher magnification makes the image more prone to hand shake, requiring a steady hand or tripod for best results. The narrower field of view compared to 8x magnification may make it slightly more challenging to locate and track moving objects.
When to Choose 10x: Choose 10x magnification when you want to observe greater detail and are willing to sacrifice a slightly wider field of view. These binoculars are suitable for activities that require more precise vision, such as birdwatching, hunting, and sports events.
12x Magnification
Advantages: Binoculars with 12x magnification provide even greater detail and closer views of distant objects. They are excellent for observing fine details in a variety of scenarios and excel in nature observation and long-range terrestrial use.
Disadvantages: The higher magnification amplifies hand shake, and image stability can be more challenging to achieve without the use of a tripod. They tend to have a narrower field of view, making it more difficult to locate and track fast-moving objects. Additionally, the image may appear dimmer in low-light situations due to the larger magnification.
Which Magnification is Best?
When to Choose 12x: Opt for 12x magnification when you require maximum detail and close-up views of distant objects. These binoculars are suitable for activities such as astronomy, long-range terrestrial observation, and surveillance.
When choosing between magnifications, consider the trade-offs between the field of view, detail, stability, and ease of use. Consider the specific activities and environments in which you will be using the binoculars to determine the most suitable magnification for your needs.
The Role of Objective Lens Diameter
The objective lens diameter in binoculars plays a crucial role in determining the quality of the image you see and the overall performance of the binoculars. The diameter of the objective lens is typically measured in millimeters and is represented by the second number in the binocular specifications, such as “8×42” or “10×50″12.
The objective lens is responsible for gathering light and directing it to the eyepiece. A larger objective lens diameter allows more light to enter the binoculars, leading to a brighter image with enhanced clarity and contrast. This is especially important in low-light conditions, such as dawn or dusk, where a larger objective lens diameter can significantly improve the visibility of the observed objects23.
In addition to providing a brighter image, a larger objective lens diameter also allows for a wider field of view2. A wider field of view means you can see more of the surrounding area through the binoculars, making it easier to locate and track objects, especially when observing fast-moving subjects such as birds or wildlife1.
However, there are a few trade-offs to consider when it comes to the objective lens diameter. Binoculars with larger objective lenses tend to be bulkier, heavier, and more expensive compared to those with smaller objective lenses2. The larger size and weight may make them less portable and convenient for long periods of use.
In summary, the objective lens diameter of binoculars plays a critical role in determining the amount of light gathered, the brightness of the image, the field of view, and overall low-light performance. Selecting the appropriate objective lens diameter depends on your specific needs and preferences, balancing factors such as brightness, portability, and cost.
Unveiling the Angle of View and Field of View
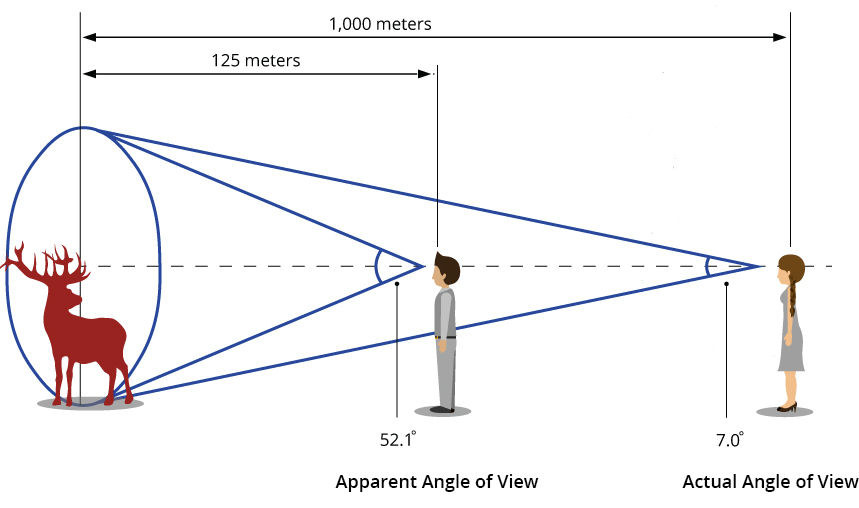
The concepts of “angle of view” and “field of view” are essential in understanding how far you can see with 10×50 binoculars. The angle of view refers to the angular extent of the scene that is visible through the binoculars. It is typically measured in degrees and provides an indication of how wide or narrow the observable scene is.
The field of view, on the other hand, is a measure of the linear extent of the scene that can be observed at a specific distance. It is usually expressed in feet or meters and indicates the width of the observable scene at a given distance. A wider field of view allows you to capture larger areas without needing to constantly readjust the binoculars.
While the angle of view and field of view can vary among different binocular models, 10×50 binoculars generally offer a wider angle of view compared to higher magnification models. This wider angle of view allows for a larger observable scene, making it easier to locate and track objects over a wider area.
In this case, “10x” means that the binoculars can make objects appear ten times closer than they actually are, enabling observers to see fine details at greater distances.
Determining the Maximum Distance
Now, it’s time to address the core question: how far can you see with 10×50 binoculars? The actual maximum distance at which you can see objects with these binoculars depends on several factors, including atmospheric conditions, inanimate obstructions, and human visual acuity.
While it is challenging to provide an exact distance, some sources suggest that 10×50 binoculars have a potential range of between 2.5 to 10 miles. However, it’s important to remember that these estimates are subject to various factors and may vary from person to person.
Beyond Distance: Other Considerations
While distance is undoubtedly a consideration when discussing the capabilities of binoculars, it is important to remember that binoculars offer more than just the ability to see objects at a particular distance. They provide a window into the world, revealing intricate details, textures, and colors that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Furthermore, 10×50 binoculars are versatile tools suitable for a variety of outdoor activities, such as birdwatching, hunting, sports events, and even astronomy. Their combination of magnification power, objective lens diameter, and optical quality allows for an enhanced viewing experience, regardless of the subject or distance.
Conclusion: Expanding Our Vision
In conclusion, the capabilities of 10×50 binoculars extend far beyond specific numerical values and maximum distances. They are a testament to the ingenuity of early inventors and the advancements in optical technology. As we navigate the complexities of magnification, lens specifications, and concepts like angle of view and field of view, we gain a deeper understanding of how binoculars enhance our vision and connect us with the world around us.
So, the next time you pick up a pair of 10×50 binoculars, remember that it’s not just about seeing far; it’s about expanding our vision, appreciating the beauty of our environment, and exploring new horizons with clarity and purpose.
Obviously, binoculars are used to see objects at a distance.
The telescope was invented about 400 years ago and binoculars are basically two telescopes that are attached.
The first number is the magnification and the second number is the size of the objective lens (the lens closest to the object you are viewing).
So, in this post, we are going to see how far a 10x magnification with a 50mm objective lense can see.

Awesome research. I’m amazed by the article and the picture it really explains it all. Thank you.
Amazing info ! I’ve never learned any of this previously. Very beneficial. Thank you .
Thank you
Very helpful, thank you,
Great explanation thank you
Hey Adam, Almost everyone know about binoculars and all the visual equipment used for wildlife and birdwatching, but what about enhanced hearing or ear equipment that can be used for listening to wildlife and birds outdoors!….. Just wondering if there’s any equipment or devices for outdoor listening?